Material Properties
Titanium is a chemical element, chemical symbol Ti, atomic number 22, located in the fourth period and group IVB in the periodic table of chemical elements. It is a silver white transition metal, characterized by light weight, high strength, metallic luster and resistance to wet chlorine.Product Specifications
Supply status:
Hot working state (R) cold working state (y) annealing state (m) solid solution state (st)
Titanium rod executive standard
National standards: GB / t2965-2007, GB / t13810, Q / bs5331-91
American Standard: ASTM b348, ASTM F136, ASTM F67, ams4928
Titanium classification
According to the structure after annealing, titanium alloys can be divided into three categories:
(1) α Alloy and near α Alloy.
(2)( α+β) Alloy.
(3) β Alloy and near β Alloy.
The national standard is replaced by TA α Alloy; TB representative β Alloy; TC representative( α+β) Alloy. For example, TA1 is industrial pure titanium; Tb1 is β Titanium alloy; TC4 is( α+β) Titanium alloy. Most of the newly developed alloys directly follow American standards and are expressed by alloy elements and contents. For example, Ti-1023 alloy is based on titanium and contains 10% vanadium, 2% iron and 3% aluminum.
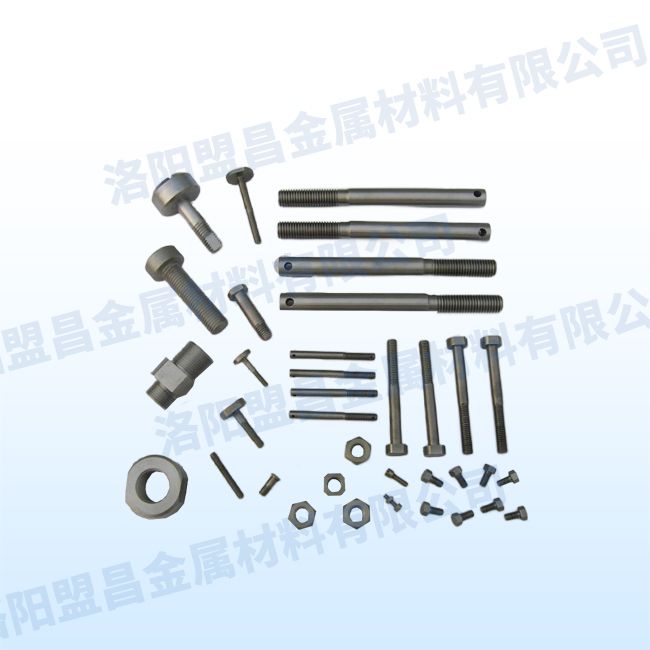
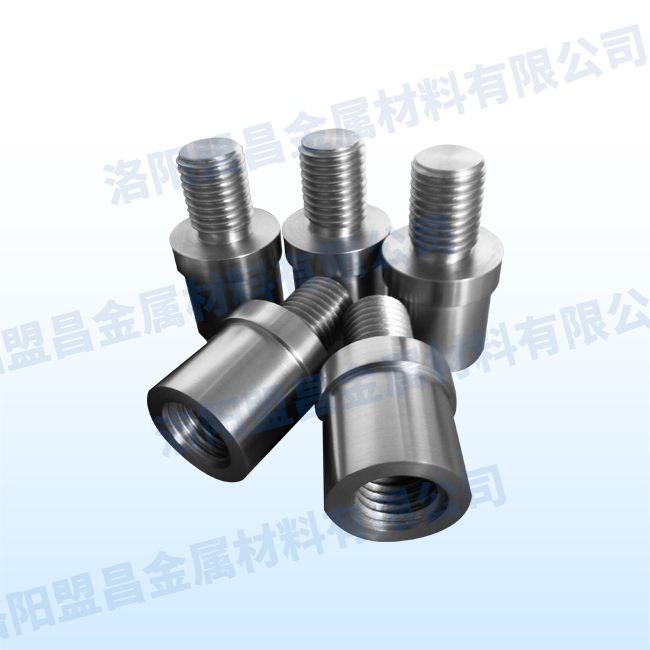
Other Products



 TEL
TEL skype
skype Message
Message